

Enlargement using a negative scale factor
I can perform a given enlargement on an object.


Enlargement using a negative scale factor
I can perform a given enlargement on an object.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Each length in the shape is multiplied by the scale factor.
- Each vertex in the object is a given distance from the centre of enlargement.
- This distance is also multiplied by the scale factor to give the distance of the image's vertex.
- A negative scale factor produces an image that is the other side of centre of enlargement.
- To enlarge, you need the centre of enlargement and a scale factor.
Keywords
Transformation - A transformation is a process that may change the size, orientation or position of a shape.
Enlargement - Enlargement is a transformation that causes a change of size.
Scale factor - A scale factor is the multiplier between similar shapes that describes how large one shape is compared to the other.
Centre of enlargement - The centre of enlargement is the point from which a shape is enlarged.
Common misconception
Pupils may think that a negative scale factor creates a smaller image than the object.
Remind them that the absolute value will be less than 1 and greater than 0 to create a smaller image. Whether the scale factor is positive or negative does not affect this.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A transformation is a process that may change the , orientation or position of a shape.
Q2.Shape B is enlarged to give shape A. What is the scale factor of this enlargement?

Q3.Three Oak pupils enlarge the same shape. Whose diagrams are incorrect?



Q4.Shape B is enlarged to give shape A. What is the scale factor of this enlargement?

Q5.Shape B is enlarged to give shape A. The centre of the enlargement is at (-3, ).

Q6.Describe the transformation that maps shape A onto shape B.

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.When the scale factor of an enlargement is negative, the image is a rotation of ° of the object.
Q2.Which diagram shows an enlargement by a negative scale factor?
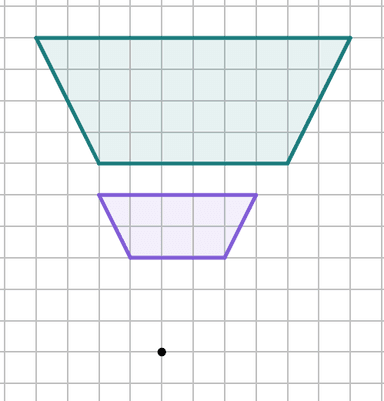
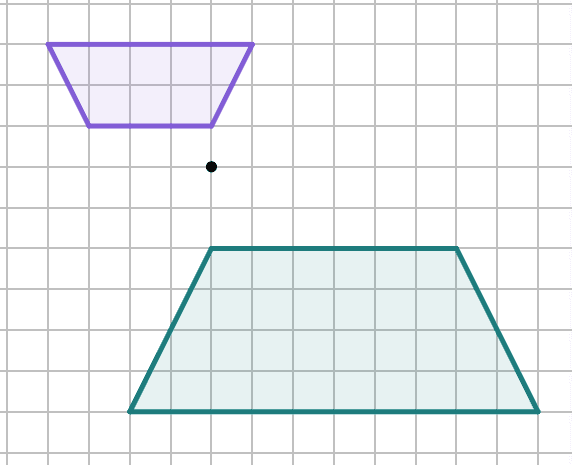
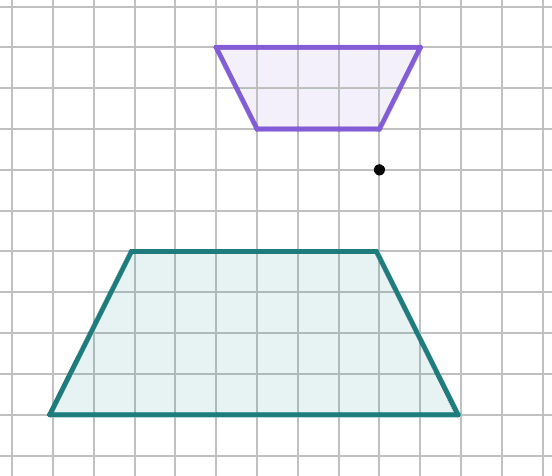
Q3.Laura says, "When you enlarge an object by a fractional scale factor, the image is always smaller than the object." Is Laura correct? Justify your answer.
Q4.Shape A is enlarged to give shape B. The scale factor of this enlargement is .
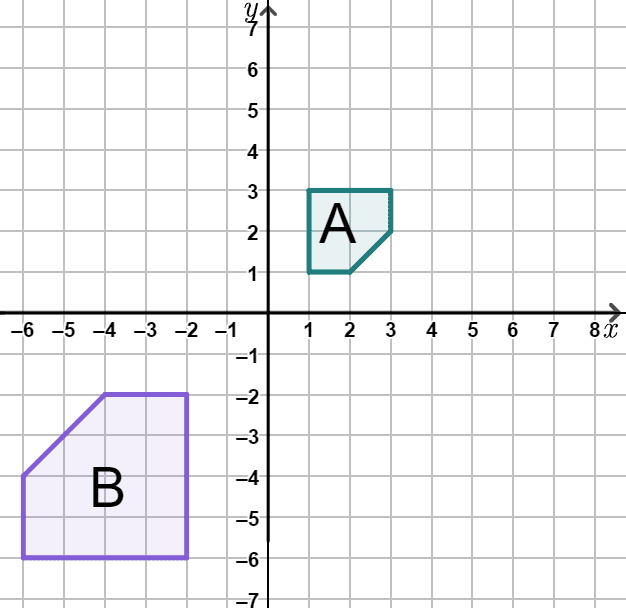
Q5.Shape A is enlarged to give shape B. The centre of enlargement is at the .

Q6.Shape A is transformed to give shape B. Describe the transformation.


