Lesson 4 of 11
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- In this lesson, we will be introduced to one of two searching algorithms we need to know about: linear search. We will go over the steps of carrying out a linear search, and perform a linear search in real life and with a sample of data.
Licence
This content is made available by Oak National Academy Limited and its partners and licensed under Oak’s terms & conditions (Collection 1), except where otherwise stated.
4 Questions
Q1.'Calculates the remainder of a division.'
'Calculates the remainder of a division.'
Integer division
Q2.'Calculates the whole number of times the divisor will go into the dividend '
'Calculates the whole number of times the divisor will go into the dividend '
Modulo (MOD)
Q3.State the result of the following calculation in Python: 14 % 4
State the result of the following calculation in Python: 14 % 4
1
3
4
Q4.State the result of the following calculation in Python: 28 // 5
State the result of the following calculation in Python: 28 // 5
6
8
9
4 Questions
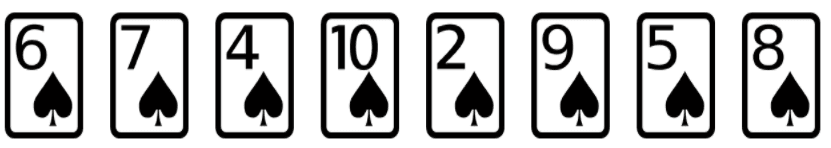
Q1.What card would you need to search for, for the best-case scenario to occur?
What card would you need to search for, for the best-case scenario to occur?
10
7
8
9
Q2.What card would you need to search for, for the worst-case scenario to occur?
What card would you need to search for, for the worst-case scenario to occur?
10
6
7
9
Q3.How many comparisons would it take to work out that a card wasn’t in the set of cards?
How many comparisons would it take to work out that a card wasn’t in the set of cards?
10
6
7
9
Q4.When carrying out the linear search, does the data need to be ordered?
When carrying out the linear search, does the data need to be ordered?
Yes

