Cells
I can identify that all cells have some structures in common and I can explain that all organisms are unicellular or multicellular.
Cells
I can identify that all cells have some structures in common and I can explain that all organisms are unicellular or multicellular.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- All organisms (including animals, plants, fungi and micro-organisms) are made up of one or more living cells.
- All cells have some structures in common (cell membrane and cytoplasm) and have a three-dimensional shape.
- Chemical reactions essential to life occur in cytoplasm; the cell membrane regulates the cell’s internal environment.
- Many animals and plants are multicellular; they are made up of many cells organised to form tissues and organs.
- Micro-organisms such as bacteria are unicellular – they are made of just one cell.
Keywords
Organism - A living thing made of one or more cells.
Cell - The basic unit of all forms of life.
Multicellular - An organism made of many cells.
Micro-organism - An organism that can only be viewed through a microscope.
Unicellular - An organism that consists of a single cell.
Common misconception
Pupils may think that all animals and plant are multicellular and that all unicellular organisms are bacteria.
Lesson explicitly addresses this misconception and the questions in Task A are designed to expose the misconception.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What are all living organisms made of?
Q2.What type of cell is shown in the image?

Q3.What type of cell is shown in the image?

Q4.Shown in the image is an animal cell. What is label A pointing to?
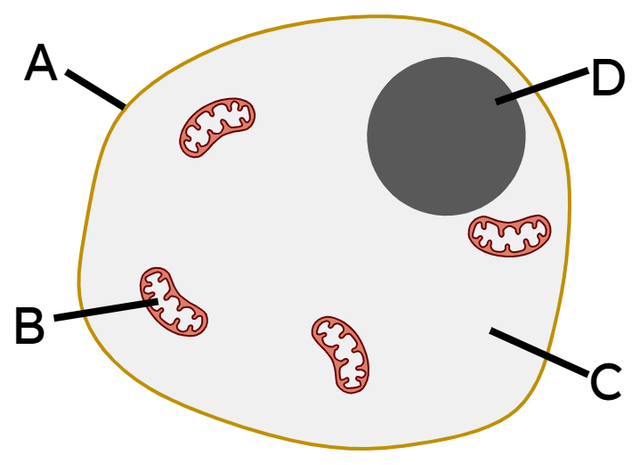
Q5.What is the function of the nucleus of a cell?
Q6.Which of the following are found in plant cells but not animal cells?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What does the term 'multicellular organism' mean?
Q2.Which of the following is true for unicellular organisms?
Q3.Starting with the smallest, sort the organisational structure of multicellular organisms into the correct order.
Q4.Which of the following are found in both plant and animal cells?
Q5.Match the following structures with their functions.
jelly-like substance where chemical reactions take place
contains DNA, which controls the cell activities
where energy is released through aerobic respiration
contains cellulose, which provides strength and support to cell
Q6.Match the following structures with their functions.
where protein synthesis occurs
controls what enters and exits the cell
contains sap which helps keep the cell turgid
contains chlorophyll, which is where photosynthesis occurs


