Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- OCR
- Higher
Monoclonal antibodies
I can explain how monoclonal antibodies are produced and describe some ways in which they are used.
- Year 11
- OCR
- Higher
Monoclonal antibodies
I can explain how monoclonal antibodies are produced and describe some ways in which they are used.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Monoclonal antibodies recognise a specific target, such as an antigen or other biological molecule.
- Monoclonal antibodies are produced by combining a lymphocyte and a tumour cell to produce a hybridoma.
- The hybridoma divides to make many copies of this single clone, which make monoclonal antibodies.
- Monoclonal antibodies are used to detect pathogen antigens & molecules associated with pregnancy, blood clots & cancer.
- Monoclonal antibodies can be attached to radioactive and toxic substances to treat diseased cells, e.g. tumour cells.
Keywords
Antigen - A molecule on the surface of a pathogen or other cell, which triggers an immune response.
Lymphocyte - A white blood cell that is part of the immune system and produces antibodies against a specific antigen.
Monoclonal antibodies - Antibodies produced from a single clone of a hybridoma.
Tumour cell - A cell that undergoes uncontrolled cell division.
Hybridoma - An antibody-producing lymphocyte and a tumour cell fused together.
Common misconception
Monoclonal antibodies can act as a 'magic bullet' to deliver medication to certain cells.
The human body is complex and therapies using monoclonal antibodies have had some serious side effects. New treatments should always be treated with caution.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Monoclonal antibodies, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Monoclonal antibodies, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Medicines and new treatments for disease unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Content guidance
- Depiction or discussion of sensitive content
Supervision
Adult supervision recommended
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following are white blood cells?
Q2.The main role of which human system is to protect us from disease?
Q3.What are the subunits of proteins?
Q4.Match the term to its meaning.
proteins produced by a type of white blood cell
the proteins on the surface of cells
white blood cells that produce antibodies
white blood cells that engulf pathogens and digest them
Q5.Select the best description of cancer.
Q6.The Oak pupils are discussing vaccination. Who is correct?




Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Antigens and antibodies are in their shape.
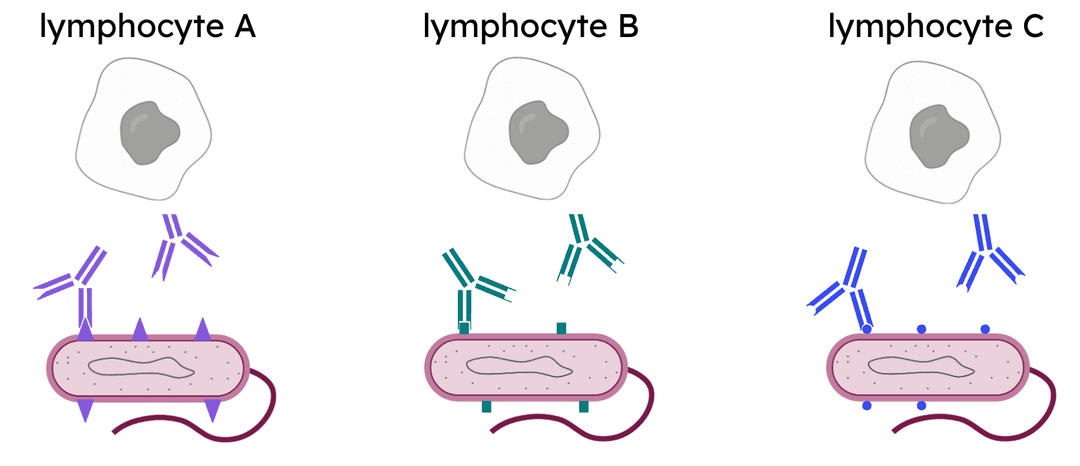
Q2.Where are lymphocytes extracted from when making monoclonal antibodies?
Q3.What is a hybridoma?
Q4.Put these steps in order to show how monoclonal antibodies are made.

Q5.Select the uses of monoclonal antibodies.
Q6.In a pregnancy test what is the monoclonal antibody attaching to?



