Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- Higher
Dividing vectors into ratios
I can solve geometric problems in 2D where vectors are divided in a given ratio.


- Year 11•
- Higher
Dividing vectors into ratios
I can solve geometric problems in 2D where vectors are divided in a given ratio.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A vector can be divided into parts using a ratio.
- By converting the ratio to a fraction, you can express each part in terms of the original vector.
- This allows you to perform further manipulations.
Keywords
Vector - A vector can be used to describe a translation.
Displacement - Displacement is the distance from the starting point when measured in a straight line.
Resultant vector - A resultant vector is the single vector that produces the same effect as a combination of other vectors.
Common misconception
When calculating the resultant vector, pupils can incorrectly sum vectors due to opposite directions or proportions of vectors.
Encourage pupils to write a clear vector pathway, sometimes using highlighters can help visualise this pathway.
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Dividing vectors into ratios, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Dividing vectors into ratios, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Vectors unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Work out the resultant vector for $${10 \choose -2} + {4 \choose 9}$$.
Q2.Match each notation to its correct meaning.
$$\overrightarrow{OX}$$ -
A vector starting from $$O$$ and ending at $$X$$
$$OX$$ -
A line segment with points $$O$$ and $$X$$ at each end
$$\overrightarrow{XO}$$ -
A vector starting from $$X$$ and ending at $$O$$
$$\overrightarrow{XY}$$ -
A vector starting from $$X$$ and ending at $$Y$$
$$XY$$ -
A line segment with points $$X$$ and $$Y$$ at each end
Q3.Match each vector to an equivalent vector statement.
$${12 \choose -9}$$ -
$$3\times {4 \choose -3}$$
$${16 \choose -12}$$ -
$$4\times {4 \choose -3}$$
$${-18 \choose -6}$$ -
$$2\times {-9 \choose -3}$$
$${4\choose -20}$$ -
$$-2\times {-2 \choose 10}$$
$${-27\choose -27}$$ -
$$-3\times {9 \choose 9}$$
Q4.Match each vector statement to an equivalent vector statement.
$$5\mathbf{a}+2\mathbf{b}$$ -
$$\frac{1}{2}(10\mathbf{a}+4\mathbf{b})$$
$$4\mathbf{a}+2\mathbf{b}$$ -
$$\frac{1}{3}(12\mathbf{a}+6\mathbf{b})$$
$$2\mathbf{a}+3\mathbf{b}$$ -
$$\frac{1}{5}(10\mathbf{a}+15\mathbf{b})$$
$$5\mathbf{a}-2\mathbf{b}$$ -
$$\frac{1}{2}(10\mathbf{a}-4\mathbf{b})$$
$$15\mathbf{a}-12\mathbf{b}$$ -
$$\frac{3}{4}(20\mathbf{a}-16\mathbf{b})$$
Q5.Select the vector path for $$\overrightarrow{AD}$$.
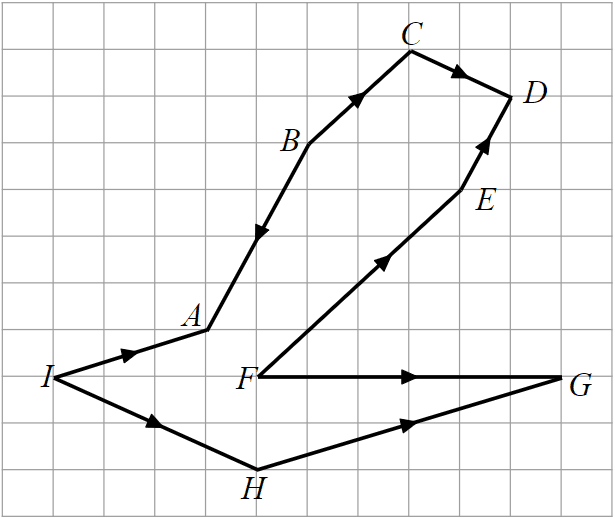
Q6.Select the statements which are true.

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.X is a point on a line AB. Match each vector statement to the correct ratio.
$$AX:XB \; \text{is} \; 1:4$$ -
$$\frac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{AX}$$
$$AX:XB \; \text{is} \; 1:3$$ -
$$\frac{1}{4}\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{AX}$$
$$AX:XB \; \text{is} \; 1:1$$ -
$$\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{AX}$$
$$AX:XB \; \text{is} \; 4 : 1$$ -
$$\frac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{AX}$$
$$AX:XB \; \text{is} \; 2 : 3$$ -
$$\frac{2}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{AX}$$
Q2.B is a point on the line OL. Match each ratio to the correct vector statement.
$$OB : BL \; \text{is} \; 1 : 5$$ -
$$\frac{1}{6}\overrightarrow{OL}=\overrightarrow{OB}$$
$$OB : BL \; \text{is} \; 1 : 1$$ -
$$\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{OL}=\overrightarrow{OB}$$
$$OB : BL \; \text{is} \; 11 : 1$$ -
$$\frac{11}{12}\overrightarrow{OL}=\overrightarrow{OB}$$
$$OB : BL \; \text{is} \; 1 : 11$$ -
$$\frac{1}{12}\overrightarrow{OL}=\overrightarrow{OB}$$

