Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 8
Changing speed
I can describe how the speed of an object changes throughout the time that a resultant force is acting on it.
- Year 8
Changing speed
I can describe how the speed of an object changes throughout the time that a resultant force is acting on it.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A resultant force can change the speed of an object.
- The speed of an object changes throughout the time a resultant force is acting on it.
- The greater the gradient (steeper the line) on a distance-time graph, the faster the movement.
Keywords
Resultant force - The overall effect of a set of forces acting on an object.
Speed - A measurement of how fast something is moving, found from the distance travelled divided by the time taken.
Dynamics trolley - A small wheeled cart used in motion experiments.
Acceleration - A change in speed or direction of movement.
Common misconception
Pupils can think that change in speed is instantaneous due to forces, not over a period of time.
Demonstrate that objects continue to accelerate while the force is acting. Make the force easy to understand (e.g. a pulling string).
To help you plan your year 8 science lesson on: Changing speed, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 8 science lesson on: Changing speed, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 science lessons from the Moving by force unit, dive into the full secondary science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Lesson video
Loading...
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of these is a force measurement?
Q2.What feature of a distance-time graphs shows the speed?

Q3.Which of these show how forces should be represented on diagram?
Q4.Ben pushes a shopping trolley so it is moving quickly but then falls and lets go. Which of these forces still act on the trolley after he has let go?

Q5.A student is measuring the average speed of a trolley between two points marked on a ramp. Which measurements do they need to make to find the speed?

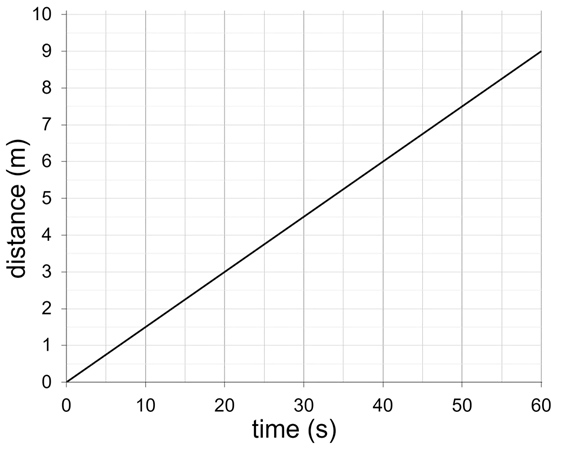
Q6.What is the average speed of this object?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the key word with the description.

The sum of forces on an object, accounting for direction.
The steepness of a line on a graph.
Distance divided by time.
A wheeled device used in motion experiments.
A change in speed.
Q2.Which of the following are acceleration?
Q3.A person drags a box along the ground using a force of 25 N towards the right. A frictional force of 20 N acts on the box as it is dragged. What is the resultant force on the box?

Q4.A sprinter takes part in a 100 m race. Which statement describes how the forces change during the race?

Q5.The figure shows a distance-time graph for a car. What does the graph show?

